Stepper motor controllers
We offer stepper motor controllers for full line of stepmotors - from tiny motors 20 mm size up to high torque stepper motors 130 mm size. Current per phase from 0.1 Amp to 8.0 Amp.

SMSD‑1.5Modbus ver.3
Programmable stepper motor controller
Voltage
12 - 36 VDC
Max. current per phase
0.15 - 1.5 A
Microstepping
1/1 - 1/256
Control methods
program, potentiometer, STEP/DIR
Interfaces
USB, RS-485 (Modbus ASCII/RTU)
SMSD‑1.5Modbus ver.3 is a programmable stepper motor controller with extended functionality. The controller can act as a master or slave in an RS-485 Modbus network, capable of controlling external devices or receiving control commands from a PLC via the Modbus RTU/ASCII protocol. It also supports standalone operation according to a predefined user program. Auto-feed function provides a high-throughput automated operation of an industrial machine. The controller provides microstepping 1/1 to 1/256. The morphing function provides a smooth transition from microstepping mode to full-step mode at a given speed, thereby maintaining torque at high speeds. Overheating protection is provided.

SMSD‑4.2Modbus
Programmable stepper motor controller
Voltage
12 - 48 VDC
Max. current per phase
1 - 4.2 A
Microstepping
1/1 - 1/256
Control methods
program, potentiometer, STEP/DIR
Interfaces
USB, RS-485 (Modbus ASCII/RTU)
SMSD‑4.2Modbus is a programmable stepper motor controller with extended functionality. The controller can act as a master or slave in an RS-485 Modbus network, capable of controlling external devices or receiving control commands from a PLC via the Modbus RTU/ASCII protocol. It also supports standalone operation according to a predefined user program. Auto-feed function provides a high-throughput automated operation of an industrial machine. The controller provides microstepping 1/1 to 1/256. The morphing function provides a smooth transition from microstepping mode to full-step mode at a given speed, thereby maintaining torque at high speeds. Overheating protection is provided.

SMSD‑8.0Modbus
Programmable stepper motor controller
Voltage
12 - 48 VDC
Max. current per phase
2.8 - 8.0 A
Microstepping
1/1 - 1/256
Control methods
program, potentiometer, STEP/DIR
Interfaces
USB, RS-485 (Modbus ASCII/RTU)
SMSD‑8.0Modbus is a programmable stepper motor controller with extended functionality. The controller can act as a master or slave in an RS-485 Modbus network, capable of controlling external devices or receiving control commands from a PLC via the Modbus RTU/ASCII protocol. It also supports standalone operation according to a predefined user program. Auto-feed function provides a high-throughput automated operation of an industrial machine. The controller provides microstepping 1/1 to 1/256. The morphing function provides a smooth transition from microstepping mode to full-step mode at a given speed, thereby maintaining torque at high speeds. Overheating protection is provided.

SMSD‑4.2LAN
Stepper motor controller
Voltage
24 - 48 VDC
Max. current per phase
0.1 - 4.2 A
Microstepping
1/1 - 1/128
Control methods
program, analog input, STEP/DIR
Interfaces
Ethernet TCP/IP, USB
SMSD‑4.2LAN can be controlled by commands via Ethernet TCP/IP, so it can be connected to a local network, which makes it possible to control the drive remotely. The controller provides 5 control methods: real-time control by commands, program mode, STEP/DIR, analog speed or position control. The controller supports standalone operation according to a predefined user program. Auto-feed function provides a high-throughput automated operation of an industrial machine.
Two versions of firmware are available for the controllers SMSD‑4.2LAN – standard and Modbus TCP/IP.The Modbus TCP/IP version is available only on demand and must be specifically indicated when placing an order.

SMSD‑8.0LAN
Stepper motor controller
Voltage
24 - 48 VDC
Max. current per phase
1.0 - 8.0 A
Microstepping
1/1 - 1/128
Control methods
program, analog input, STEP/DIR
Interfaces
Ethernet TCP/IP, USB
SMSD‑8.0LAN can be controlled by commands via Ethernet TCP/IP, so it can be connected to a local network, which makes it possible to control the drive remotely. The controller provides 5 control methods: real-time control by commands, program mode, STEP/DIR, analog speed or position control. The controller supports standalone operation according to a predefined user program. Auto-feed function provides a high-throughput automated operation of an industrial machine.
Two versions of firmware are available for the controllers SMSD‑8.0LAN – standard and Modbus TCP/IP.The Modbus TCP/IP version is available only on demand and must be specifically indicated when placing an order.

SMSD‑4.2CAN
Stepper motor controller
Voltage
12 - 48 VDC
Max. current per phase
1.0 - 4.2 A
Microstepping
1/1 - 1/128
Control methods
CANOpen, STEP/DIR
Interfaces
CAN, USB
SMSD‑4.2CAN is intended for operation under the control of a PLC with CANopen protocol. It provides velocity and position control and homing function according to the standard. The controller provides USB connection and free software for parametrization. STEP/DIR pulse position control is also provided.

SMSD‑4.2RS
Stepper motor controller
Voltage
12 - 48 VDC
Max. current per phase
0.2 - 4.2 A
Microstepping
1/1 - 1/16
Control methods
program, analog input, STEP/DIR
Interfaces
RS-485, RS-232
The controller provides both communication interfaces RS‑232 and RS‑485 for programming and real-time control via PC or PLC. Analog speed regulation and standard STEP/DIR mode are also provided. The controller can work as a standalone device or be a PLC (PC) controlled slave.
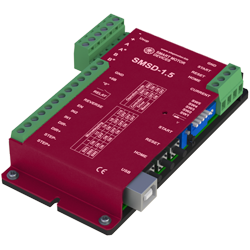
SMSD‑1.5
Stepper motor controller
Voltage
12 - 24 VDC
Max. current per phase
0.16 - 1.6 A
Microstepping
1/2 - 1/16
Control methods
program, analog input, STEP/DIR
Interfaces
USB
SMSD‑1.5 stepper motor controller is designed to control small size stepper motors, output current is under 1.6 A per motor's phase. The controller provides 3 main control modes - programmable, analog speed control and STEP/DIR position control. Digital I/O of the controller make it easy to use the controller together with other electronics of a system.
Stepper motor speed and position control
Stepper motors, renowned for their ubiquity, have found themselves indispensably intertwined within multifarious applications that demand nothing short of exacting control and precise positioning. These motors operate by converting electrical pulses into rotational stepper motion, with each pulse resulting in a fixed angular movement or step. Controlling stepper motors involves using a stepper motor controller, which offers advantages and disadvantages compared to brushless DC (BLDC) motors.
One of the significant advantages is their stepper motor position control. By controlling the number of steps, it's possible to achieve accurate positioning and control over the motor's movement. This makes stepper motors ideal for applications such as robotics, automation, and 3D printers that require precise and repeatable motion.
Stepper motors also provide excellent holding torque. When the motor is not moving, it can hold its position with high torque, which is essential in applications where the motor needs to maintain a specific position even without power. This characteristic eliminates the need for additional mechanical braking or locking mechanisms in certain scenarios.
Moreover, stepper motors offer a wide range of speed control options. By adjusting the frequency of the electrical pulses, the speed of the motor can be controlled. Stepper motor controllers provide various stepper motor speed control methods, such as microstepping, which allows for smoother and more precise motion. Additionally, some controllers offer stepper motor speed control, acceleration and deceleration profiles to achieve gradual changes in speed, reducing vibrations and improving overall performance.
Despite their advantages, stepper motors have some limitations compared to BLDC motors. One major drawback is their lower efficiency. Stepper motors, by their very nature, have a propensity for consuming an amplified magnitude of power, particularly when traversing the realms of swifter velocities or under heavy loads. This can result in increased energy consumption and heat generation, requiring additional cooling measures in certain applications.
Another limitation is the limited high-speed capability of stepper motors. Due to their step-by-step movement, stepper motors are not well-suited for applications that require continuous high-speed rotation. BLDC motors, on the other hand, excel in such scenarios, offering smooth and continuous motion at high speeds.
To step motor control effectively, stepper motor driver are necessary. These drivers generate the required pulse signals to drive the motor and determine its speed and direction.
Programmable stepper motor controller offer advanced features and flexibility. This controller allow for precise control over acceleration, deceleration, and speed profiles. Additionally, programmable controllers can incorporate feedback mechanisms to achieve closed-loop control, ensuring accurate position and motion control.
When purchasing a stepper motor controller, it's important to consider factors such as the number of motor phases, the motor's current and voltage ratings, and the required control interface. Controllers are available for different motor types, including bipolar and unipolar stepper motors, and can operate at various voltage levels, such as 24v motor controller.
In summary, stepper motors provide precise position control, excellent holding torque, and a range of speed control options. However, they have lower efficiency and limited high-speed capabilities compared to BLDC motors. Stepper motor controllers, including programmable options, allow for advanced control over motor motion and enable features like microstepping and closed-loop control. When buying a stepper motor controller, it's important to consider motor specifications and control requirements to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.